Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
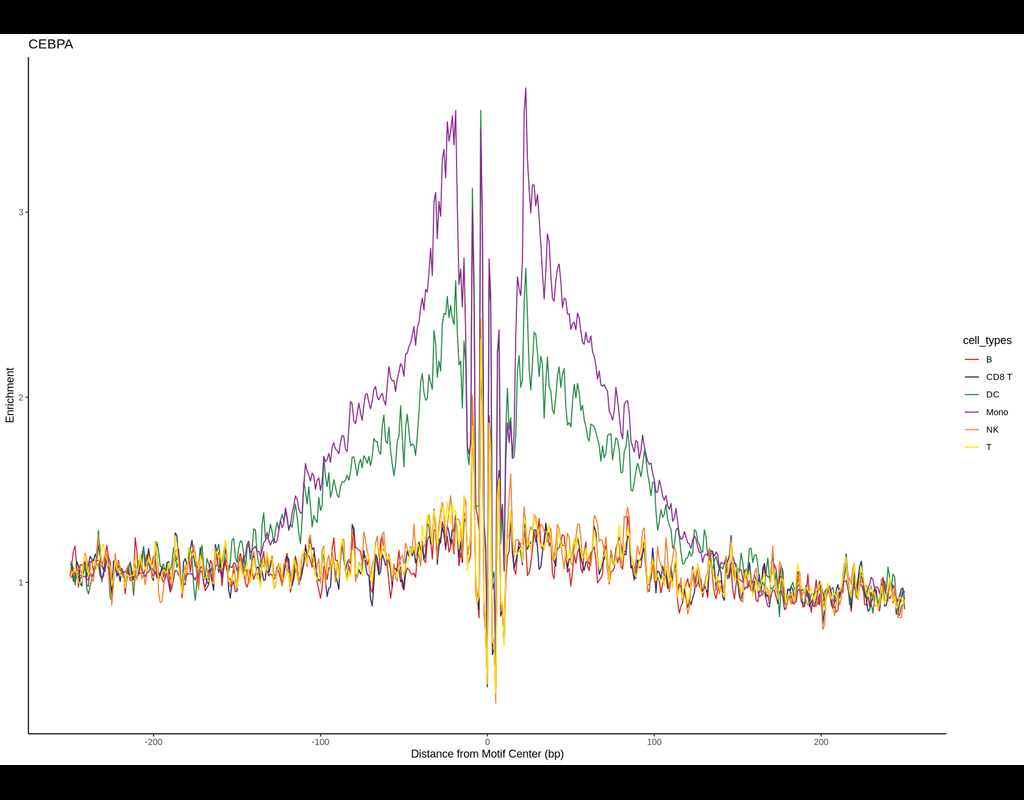
BPCells is a package for high performance single cell analysis on RNA-seq and ATAC-seq datasets. It can analyze a 1.3M cell dataset with 2GB of RAM in under 10 minutes. This makes analysis of million-cell datasets practical on a laptop.
BPCells pr(More)