Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
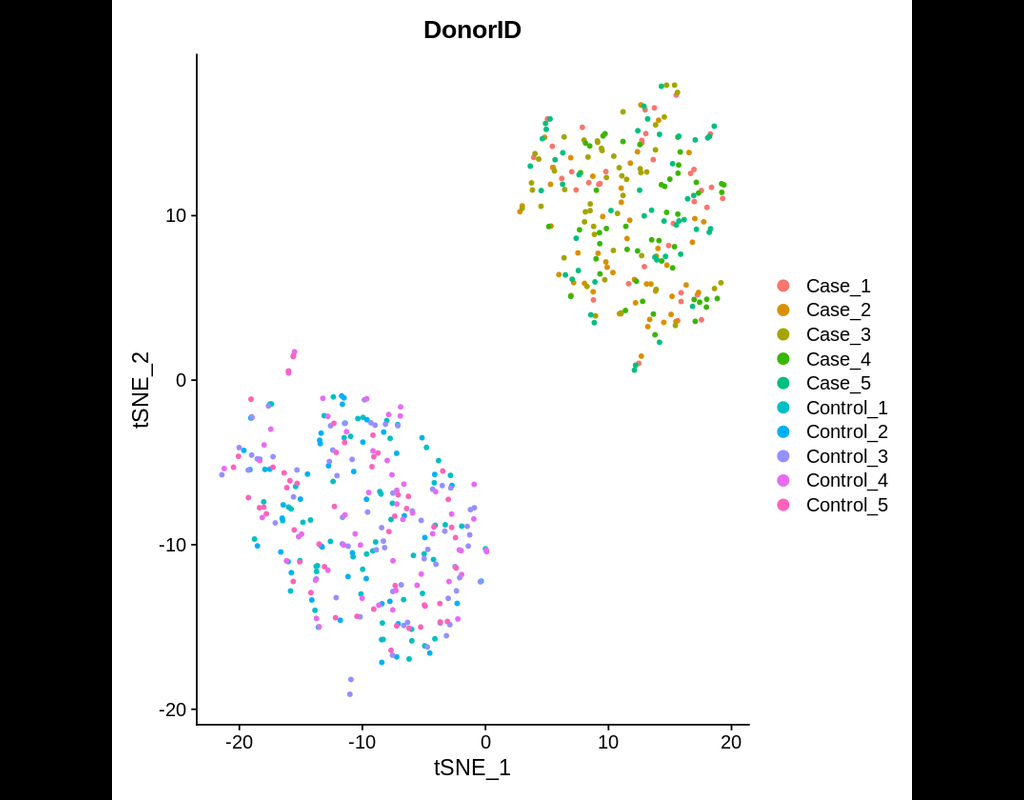
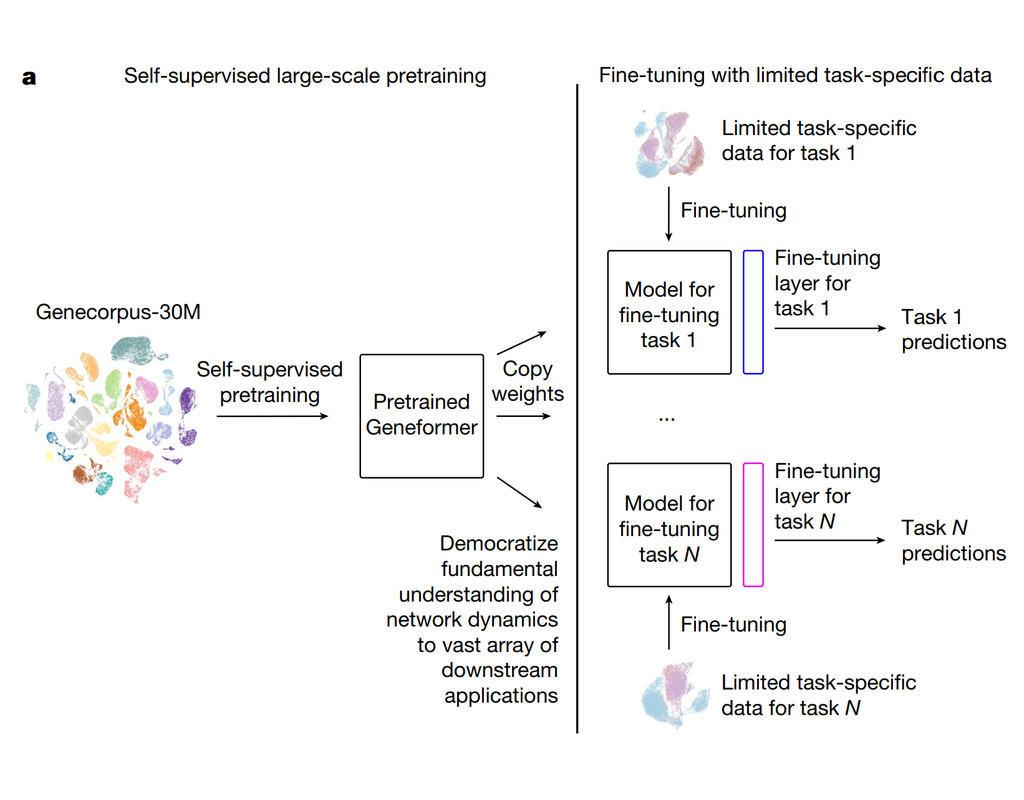
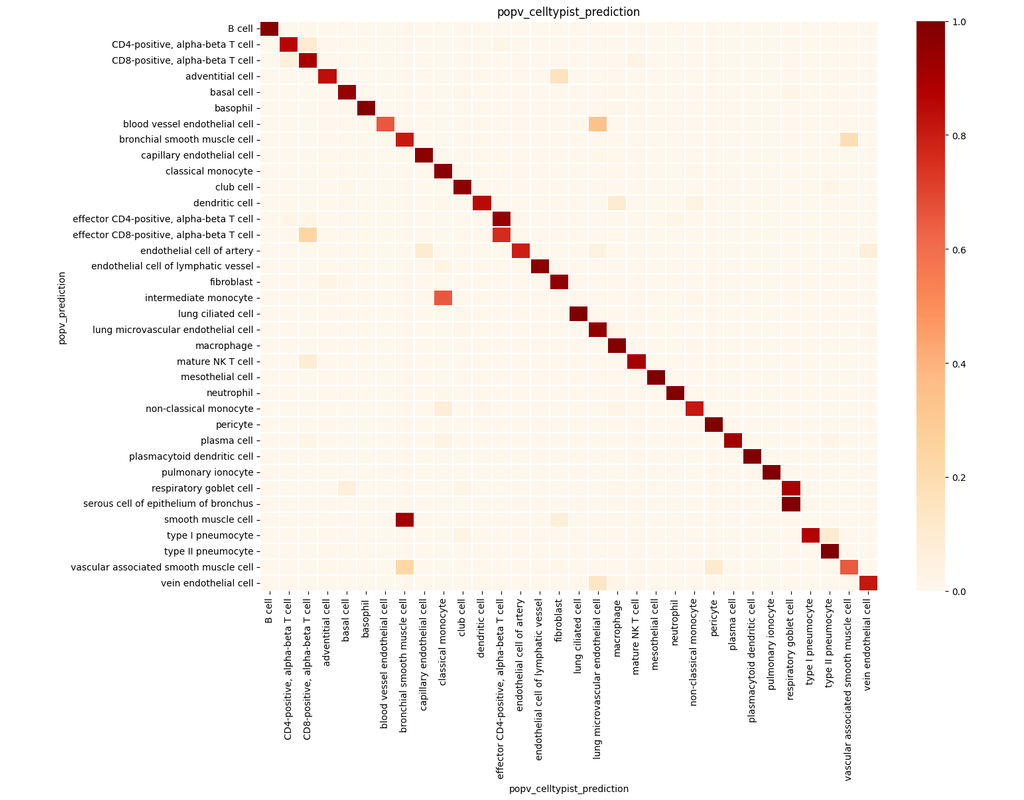
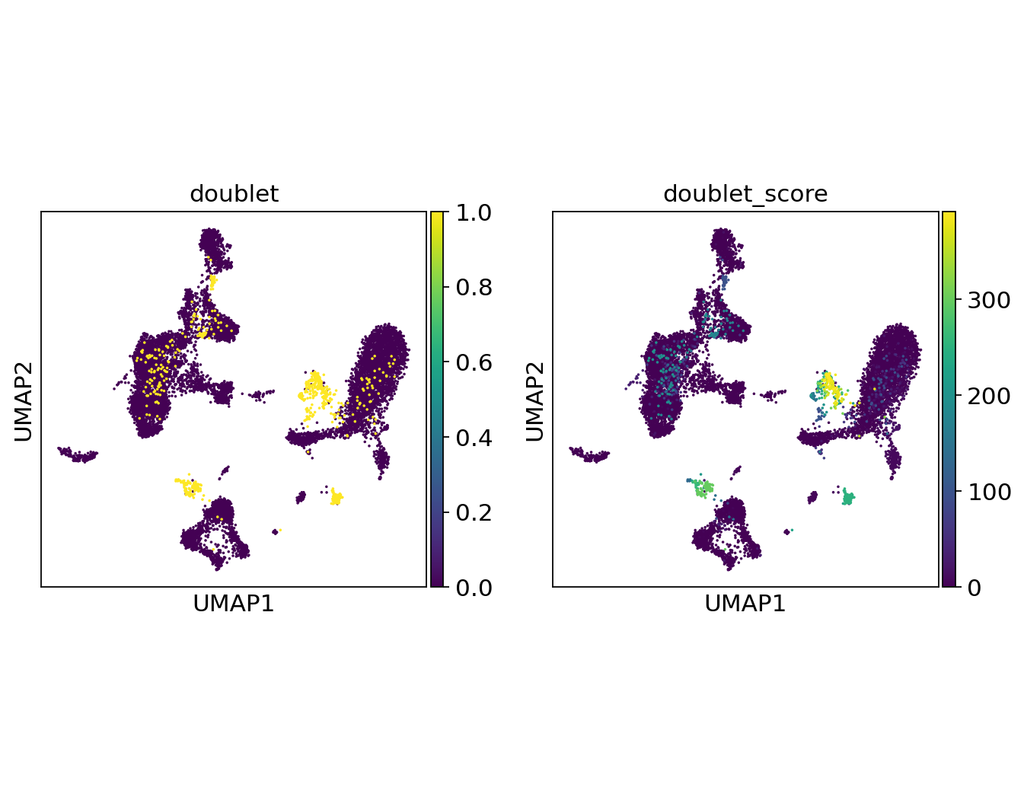
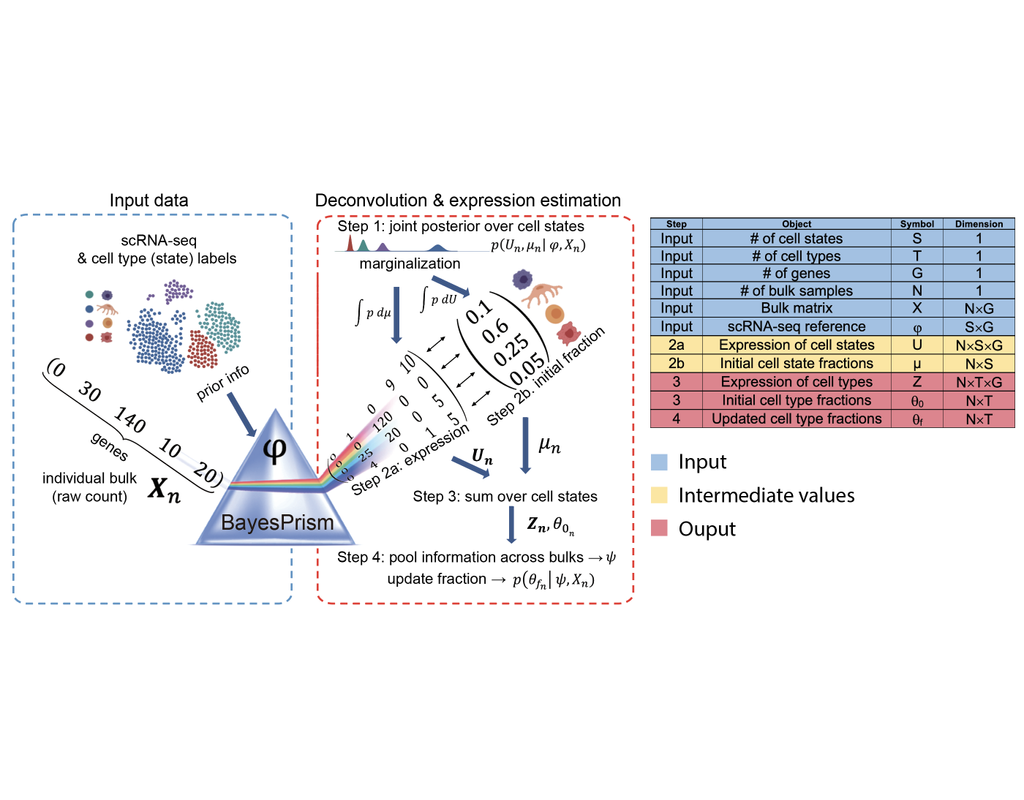
Reconstructing cell type compositions and their gene expression from bulk RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) datasets is an ongoing challenge in cancer research. BayesPrism (Chu, T., Wang, Z., Pe’er, D. et al., 2022) is a Bayesian method used to predict cell(More)